How To Perform A Heteroskedasticity Test
If statistics were perfect (as you sometimes see on your statistics books), all your data would always follow a nice straight line and you would never have any errors. However, as you already know, in the real world, things just don’t go that way. The truth is that data can be all over the place and follow a rhyme or reason we didn’t predict. This is the reason why you need to look for patterns in the data using test-statistics and regressions.
You can find the best statistics calculators at StatCalculators.
As you can easily understand, to use those statistics, you usually need to meet the assumption that your data is homoskedastic. This means that the variance of the error term is consistent across all measures of the model. Besides, it also means that the data is not heteroskedastic.
How To Perform A Heteroskedasticity Test
There are a couple of ways to test for heteroskedasticity. So, let’s check a couple of them:
#1: Visual Test:
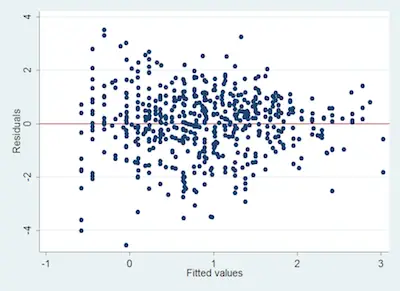
The easiest way to do a heteroskedasticity test is to simply get a good look at your data. Ideally, you generally want your data to follow a pattern of a line, but sometimes it doesn’t. So, the quickest way to identify heteroskedastic data is to see the shape that the plotted data take.
Don’t know how to perform a simple regression analysis?
Just check the image below that follows a general heteroskedastic pattern because it is cone-shaped:
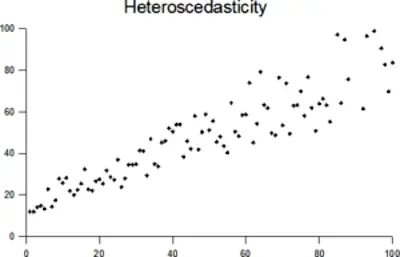
Since the variance varies, you shouldn’t perform a normal type of linear regression.
#2: Breusch-Pagan Test:
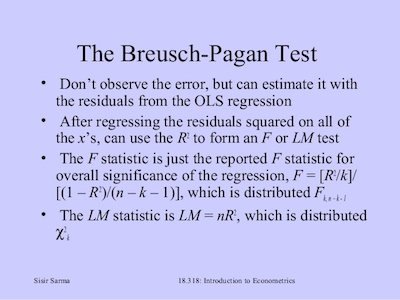
The Breusch-Pagan test is another way you have to do a heteroskedasticity test. The truth is that math is very straightforward:
χ2 = n · R2 · k
Where,
- n is the sample size
- R2 is the coefficient of determination based on a possible linear regression
- k represents the number of independent variables.
The degrees of freedom are based on the number of independent variables instead of the sample size. This test is interpreted as a normal chi-squared test.
When you get a significant result, this means that the data is heteroskedastic. Notice, however, that if the data is not normally distributed, then the Breusch-Pagan test may give you a false result.
Learn how to deal with missing data in statistics.
#3: White’s Test:
There’s no question that the White’s test is the most robust test when you are performing a heteroskedasticity test. The reality is that it tests whether all the variances are equal across your data if it is not normally distributed. Notice that the math may be a bit complicated but you can certainly use a statistic software to calculate it for you.
The White’s test is interpreted the same way as a chi-square test. If the test is significant, then the data is heteroskedastic. Besides, it still determines whether the variance is all equal across the data. However, the test is very general and can sometimes give false negatives.
Learn how to interpret regression coefficients.
Bottom Line
One of the most important things to keep in mind is that determining the heteroskedasticity of your data is essential for determining if you can run typical regression models on your data. Besides, there are 3 main tests you can perform to determine the heteroscedasticity.