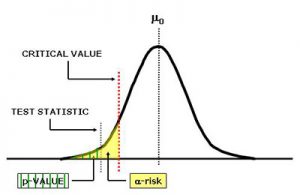
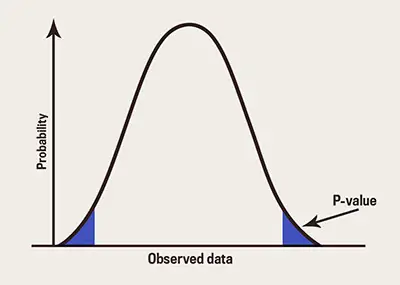
The P value is very used in statistics. Simply put, the P value is the level of marginal significance within a specific statistical hypothesis test that represents the probability of a specific event to occur.
The P value tends to be used as a different test to reject points. This way, the P value is able to provide the smallest level of significance at where the null hypothesis can be rejected.
Make sure that you use the best statistical calculators online for free.
The smaller the P value is, the stronger is the evidence in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
Calculating The P value
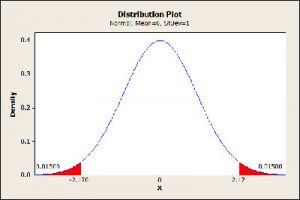
In order to calculate the P value, you need to use the P value tables or a statistical software.

One of the things that you should keep in mind is that not all researchers use the same levels of significance. So, this means that when you are examining a question, you may have some difficulties comparing the results from two different tests. So, what researchers usually do is that they tend to include the P value directly on the hypothesis test. This allows you to know and interpret the statistical significance on your own. This is often referred to as the P value approach to hypothesis testing.
Discover everything you need to know about the ANOVA F value.
P Value Approach To Hypothesis Testing
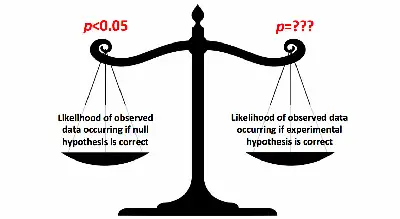
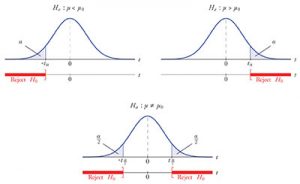
When you are looking to determine the P value this way, you will need to use the calculated probability in order to calculate if there is any evidence that allows you to reject the null hypothesis. Just as a side note, the null hypothesis is the initial claim that you make about a population of statistics.
Then, you have the alternative hypothesis. This alternative hypothesis should state if the population parameter is different from the value of the population parameter that you established on the null hypothesis.
Take a look at this reliable tool for Chi Square test.
The Type I Error
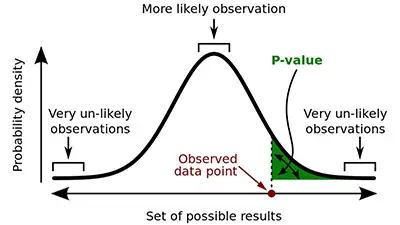
Many times, when you are reading about the P value approach to hypothesis testing you will see the mention to a type I error.
Simply put, the type I error is the false rejection of the null hypothesis. You need to understand that the probability of a type I error to occur or to reject the null hypothesis when this one is true is similar to the critical value or P value that you used. On the other hand, the probability of accepting the null hypothesis when this one is true is similar to 1 minus the critical value or P value.
Discover what range means in math.
Quick Facts About The P value
– When you are doing a statistical hypothesis test, the P value is the level of marginal significance that represents the probability of a specific event to occur.
– In order to determine or calculate the P value, you need to use either a statistical software or the P value tables.
– When you have a P value that is small, this means that there is a strong evidence of the alternative hypothesis to be accepted.