The Top Sources Of Data In Statistics
In statistics, you need to collect the figures and facts that can be numerically measured. Data, simply put, is the collection of observations that you gather that has the same characteristics.
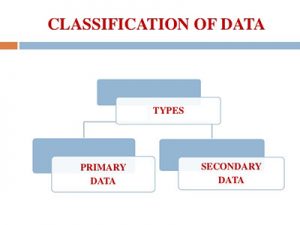
The data that you collect may be either primary data or secondary data and it can be gathered by organizations using experiments or surveys, or by individual workers. So, as you will see, there are different sources of data in statistics.
Discover the best stats calculators.
The main difference between primary and secondary data is related to the way that the data itself is gathered.
#1: Primary Data In Statistics:
Primary data is always collected wither by an individual or by an organization. This data can be gathered using different instruments including conducting interviews, focus groups, questionnaires, surveys, and experiments. We can then say that primary data is, in fact, raw data. After all, it is only collected directly and hasn’t been subjected to any statistical treatment.

Discover what range means in math.
Here are the main sources of data in statistics:
- Through Investigators:
Investigators are highly trained people whose job is to collect the data that is necessary. When doing surveys, for example, investigators will need to contact individuals and ask them to answer their questionnaires. Each one of these questionnaires should have a number of stipulated responses that should be given by the individuals. While this method can take a lot of time and be costly, there are still many organizations that adopt it because it is able to deliver good results.
- Through Personal Investigation:
This source of data in statistics is very similar to the one we just mentioned before. However, it has a limitation in case the personal investigator needs to collect a huge amount of data. After all, this will take the researcher a lot of time to get all the data he needs and he may not have the means to do all the necessary calculations.
- Through Internet:
If you are used to be online, you probably already saw adds where you can be paid for answering surveys. While not all these websites are trustworthy, this form of data collection is worth to be mentioned. After all, this is one of the main tools Google uses to collect pertinent information.
- Through Local Sources:
You probably already got some phone calls asking you to fill out a survey or a questionnaire. It can be related to a wide range of subjects. This type of data is usually one of the easiest and fastest kinds of data to obtain.
- Through Questionnaire:
A questionnaire is just a set of questions that needs to be sent out by mail (or downloaded) to the previously selected individuals. While this method is one of the most affordable ones, many people decline to answer and never mail back their questionnaire to the investigator.
Discover everything you need to know about standard deviation in statistics.
#2: Secondary Data In Statistics:
Secondary data in statistics is the type of data that is immediately available to be gathered. There is no need to ask questions to have the answers. Secondary data is available to the general public through newspapers, journals, and publications.
This kind of data may have undergone some kind of statistical treatment and can be tabulated or sorted.
Here are the sources of data in statistics:
- Research journals and newspapers
- Government Organizations such as the Census and Registration Organization, the Crop Reporting Service-Agriculture Department, the Federal and Provincial Bureau of Statistics, among many others.
- Teaching and research organizations
- Semi-Government organizations such as financial and commercial institutions, district councils, municipal committees, among others
- Internet