The Basics Of Probability
Generally speaking, when we talk about probability, we are referring to the likelihood that a certain event will occur.
Discover the best statistics calculators in 2020.
One of the things you need to know about probabilities is that they vary between 0 and 1 (or 0% and 100%). The closer the probability is to zero, the lesser the likelihood the event has of occurring. On the other hand, the closer a probability is to 1, the greater the likelihood the event will occur.
The truth is that since you have some background in statistics, probabilities are not new to you. But even if you’re just starting in statistics, if you look at the weather report for the day and see that there’s a “90% chance of rain,” you know that you should probably bring an umbrella. However, a “10% chance of rain” might prompt you to leave the umbrella at home.
So, where do these numbers come from?
Check out our binomial probability calculator.
Basics Of Probability: Certain Events And Impossible Events
As you can easily understand, when an event has a probability of 1 or 100%, we can call it a certain event. For example, in a coin toss, the probability that the coin lands either heads or tails is 100%. These are the only possible outcomes, and it’s certain that one of them will occur.
On the other hand, an impossible event has a probability of 0 or 0%. An example would the probability of drawing five kings from a fair, standard deck of 52 cards. The reason this event is impossible is because there are only four kings in the deck.
Learn more about the probability theory.
Calculating Theoretical Probability
Imagine now that you have a bag and 8 colored marbles inside, all equal in size, and weight.
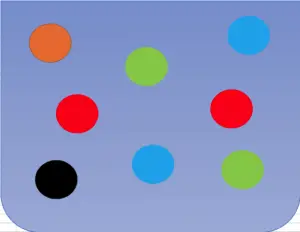
If you pick a random bag from the bag, what is the probability that it is the black marble? To determine this, you would need to use the following formula:
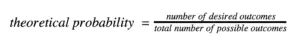
Notice that the desired outcome is what you want. In this example, it would b the black marble which means that you only have one desired outcome out of a total of 8 total possible outcomes (8 total marbles).
Therefore the probability that you pick the black marble is ⅛, or 0.125, or 12.5%. We often write this as follows:
P(black) = ⅛
Check out this overview of the most common probability math problems.
Probability And Sample Spaces
Let’s keep using the same example of the bag with 8 marbles inside. The bag and the marbles it contains can be considered a sample space.
Technically speaking, a sample space contains all the values that a random variable can take. This means that it contains all the possible outcomes. So, getting back at our example, all of the outcomes are equally likely.
Basics Of Probability: “Or”
When you are learning probabilities, it is fairly common that you need to work with the word “or”. For example, imagine that you want to find out the probability that you draw a black or a red marble from the bag.
As you can easily understand, this increases your number of desired outcomes since you now may draw a black or a red marble.
Since there is one black marble and two red marbles, the total number of desired outcomes is now three. Since the total number of possible outcomes is unchanged (the number of total marbles is constant), so:
P(black or red) = ⅜