Learn How To Calculate P Value From Z By Hand
While there are many online calculators that show you how to calculate p value from z, the truth is that it is important to understand how to make this calculation by hand.
Before we actually start with the explanation about how to calculate p value from z, it is important that you know that when you are testing a hypothesis about a specific population, you can and should use the test statistic to decide if you will reject the null hypothesis, H0. And this can be made when you already know the p value.
Make sure to check the best free statistic calculators online.
The p value is always a probability and it is linked to your critical value. On the other hand, this critical value depends on the probability of a Type I error to occur. So, what we are saying is that it measures the probability of achieving results that are at least as strong as yours if the null hypothesis (H0) is true.
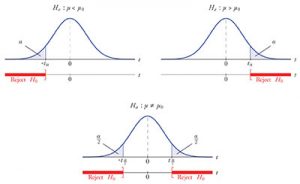
It is important to notice that in case the alternative hypothesis is the less-than alternative, in this case, you will only be able to reject the null hypothesis (H0) if your test statistic hits the left side of the distribution.
So, how to calculate p value from z?
The first thing you need to do to calculate the p value from z is to check your test statistic on the appropriate distribution – on the Z-table.
Now, looking at the Z-table, you will need to find the probability of where Z is more extreme than your test statistic. You will then be able to take one of the three possible conclusions:
#1: When Ha Contains A Less-Than Alternative:
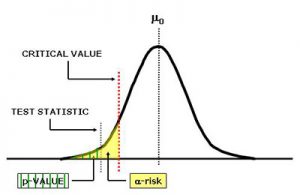
You will need to determine the probability that Z is less than your test statistic. As a side note, it is important to mention that this test statistic is usually negative.
#2: When Ha Contains A Greater-Than Alternative:
You will need to determine the probability that Z is greater than your test statistic. So, you’ll need to search for the value in the Z-table and then subtract it from one. As a side note, it is important to mention that this test statistic is usually positive.
Learn how to find Z score for a normally distributed data.
#3: When Ha Contains A Non-Equal-To Alternative:
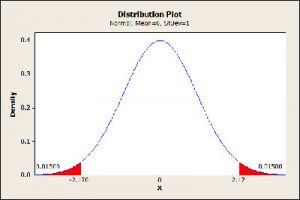
In this case, you will need to find the probability that Z is not only beyond your test statistic as you will need to double it. When this situation occurs, there can be two different scenarios:
– When your test statistic is positive, you will need to first check the test statistic on the Z-table where the Z probability is greater than your test statistic, and subtract it from one and, only then, you will double the result to get the p value.
– When your test statistic is negative, you will need to first check the test statistic on the Z-table where the Z probability is less than your test statistic and you will double it to get the p value.