Measures Of Central Tendency: Advantages & Disadvantages
One of the first things that you learn in statistics is the measures of central tendency. These include the mean, the median, the mode, and the range. However, the first three are the most important ones and these are the ones that we will be looking at today.
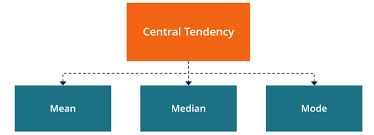
In case you don’t know or if you simply don’t remember, central tendency can be defined as the statistical measure that identifies a value that is capable of representing the entire distribution.
Learn everything you need to know about statistics.
The main goal of using measures of central tendency is to get an accurate description of the entire data. After all, when you calculate the mean, median or mode, you are looking at a value that represents the entire data.
#1: The Mean:
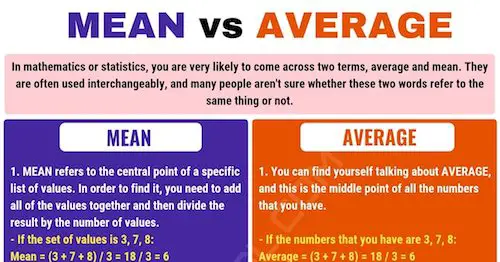
The mean can be defined in mathematical terms. After all, it is the average of all the terms. When you want to calculate the mean, you need to sum up all the values of all the terms and then divide by the number of terms.
Advantages:
- You use all the available data
- It’s a good option for ordinal or interval sets of data.
Disadvantages:
- When the set of values that you have has an extreme value, then the mean isn’t representative. For example, when you have 4 6 9 2 4 59.
Click here to use our mean, median, mode, range calculator.
#2: The Mode:
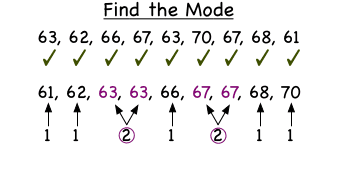
The mode can be described as the value of the term that occurs the most often. The truth is that it’s not uncommon at all for a distribution to include more than one mode, especially when there aren’t many terms. This occurs when two or more terms occur with equal frequency, and more often than any of the others.
Don’t know how to calculate mode?
Advantages:
- The mode is always a value that is actually in the set of numbers. For example, in the sequence 3 6 3 11 4 3, the mode is 3. In case you would want to calculate the mean, then this sequence has a mean of 5 which is not actually a part of the sequence.
- This is the only measure of central tendency that is useful for nominal data.
Disadvantages:
- There are occasions where you can have more than one mode which makes the data less reliable.
#3: The Median:

One of the most important things to keep in mind about the median is that it needs to be calculated differently when you have a set of values that are odd or even.
When you have an odd number of terms, then the median is the value of the term that is in the middle. On the other hand, when you have an even number of terms, then the median is the average of the two terms in the middle.
Confirm if you calculated the median the right way with our free calculator.
Notice that when you want to calculate the median, you will need to order the values from the smallest to the largest.
Advantages:
- Good to use with ordinal data.
- Anomalies and extreme values don’t tend to affect it.
Disadvantages:
- Doesn’t work well with small sets of data.