Understanding The F Test
Simply put, an F test is a kind of catch-all term for any tests that you make that use the F-distribution. In most cases, when someone is talking about an F test, they are simply talking about the F-test to compare two variances. Nevertheless, you must understand that the F-statistic is used in many different tests including the Scheffe Test, the Chow test, and even regression analysis.
Discover all the statistic calculators you can use for free.
Following The Steps To Do An F Test
In case you want to run an F test, you need to know that doing it by hand can become a bit tedious and slow. So, instead, you can use some technology to run it such as Minitab, SPSS or even Excel.
While some of the steps that we are about to show you are immediately done by technology, it is important that you know exactly what you are doing when you are running an F test.
Step #1: The first thing that you always need to do when you are running a test is to define your hypothesis. So, you will need to state both the null hypothesis as well as the alternative hypothesis.

Discover how to determine the critical F value.
Step #2: The next thing that you need to do is to calculate the F value. To do so, you will need to use the following formula:
F = (SSE1 – SSE2 / m) / SSE2 / n-k
where,
SSE = the residual sum of squares
m = the number of restrictions
k = the number of independent variables.
Use our calculator to determine the F critical value easily.
Step #3: As soon as you determine the F value, you will need to find the F statistic which is the critical value for this test. To determine the F statistic value, you can simply use the following formula:
F Statistic = variance of the group means / mean of the within-group variances
So, you can find the F statistic in the F-table.
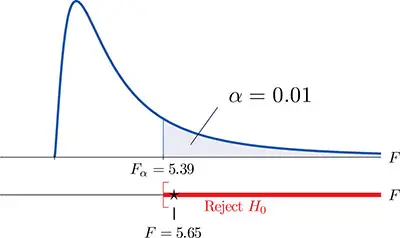
Step #4: This is the step where you can finally conclude if you support or reject the null hypothesis.
F Test T Compare Two Variances

As we already mentioned above, the statistical F test can use an F statistic to compare two variances. This is done by dividing them (s1 / s2). One of the things that you need to know is that this result is always positive.
The formula used is:
F = s21 / s22
In case the variances are equal, this means that the ration of the variances just displayed above is equal to 1.
One detail that you should always remember is that in this test, you will always be testing that the population variances are equal. So, we can also say that you always need to assume that the variances are equal to 1. So, and following what we already know, your null hypothesis will always be that the variances are equal.
Looking for a free calculator to determine the F critical value?
Assumptions
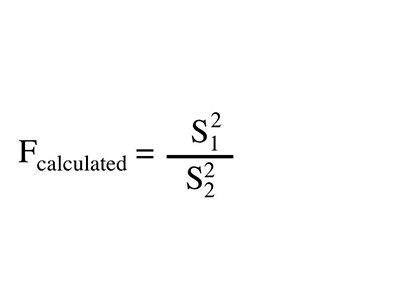
Some of the assumptions that are made for the test include:
– The larger variance that you have should always go in the numerator so that you can get a right-tailed test that us easier to calculate.
– In case you have two-tailed tests, you will need to divide alpha by 2 before you even determine the right critical value.
– In case you only have the standard deviations, you will need to square them to get the respective variances.
– In case your degrees of freedom aren’t listed in the F table, you will need to use the larger critical value to avoid any Type I errors.