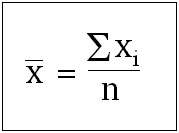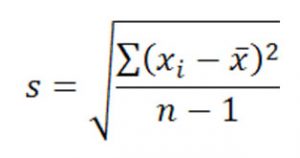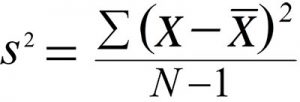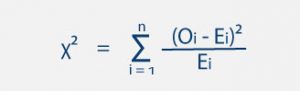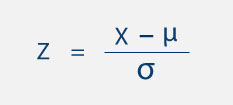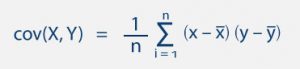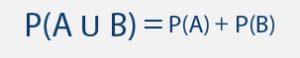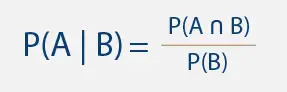Whenever you think about math or statistics in a general way, you need to understand the difference between qualitative and quantitative reasoning questions and answers.
The truth is that while most people don’t have issues with the qualitative part, most of us do have problems understanding the quantitative reasoning questions and answers.
Make sure to use the top statistics calculators.
Simply put, there are 4 different types of quantitative reasoning questions and answers. Let’s check each one in detail so that you can fully understand them.
#1: Multiple Choice: 1 Answer

The first type, and the simplest one, of quantitative reasoning questions and answers that you have, is the Multiple Choice: 1 Answer. These are simply teh traditional multiple-choice questions that you have seen all over the place.
So, all you need to do is to ensure that the answer that you get is one of the answers that you have to choose from. In case you got a different answer, you need to double-check your options. Sometimes, it is only a matter of having a number written in a different way. For example, a fraction instead of a decimal.
Discover some statistical questions examples.
#2: Multiple Choice: 1 or More Answers

The second type of quantitative reasoning questions and answers that you have is the Multiple Choice: 1 or More Answers. In this type of quantitative reasoning, you will need to find all the correct answers since there may be more than one.
So, you will need to:
- Check if the test tells you about how many correct answers there are and only choose that exact number of answers.
- In case the test doesn’t tell you how many answers it has, you can have more than one correct answer.
- All the different answers can be correct and, in that case, you need to choose them all.
- You may only have only one correct answer.
Discover the most common probability math problems.
#3: Quantitative Comparisons

Whenever you have a quantitative comparison, you will need to answer two different questions:
- How can you compare one value against the other?
- Does this happen all the time?
In order to solve these type of questions, you should consider that:
- Sometimes, it is just a matter of rewriting the expression that you have in a different way.
- Whenever you have variables, you can easily use some integers to help you.
- When you have conditions such as “if y is not equal to 0”, these are usually a good help to compare the two values.
What exactly is a statistical question?
#4: Numeric Entries
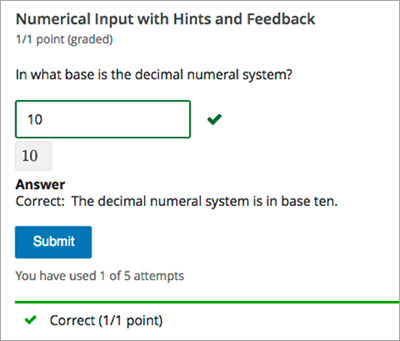
The last type of quantitative reasoning questions and answers is that numeric entries.
The truth is that in this type of questions, you won’t need to choose between different answers. You are only required to type your answer.
In order to make sure that you are able to get to the right answer, you need to carefully read the question that it is asked and understand what exactly you need to find. Then, think about how you can solve the problem and put it into practice. In the end, make sure that you take a closer look at the result and see if it makes sense.